GoldFocus - Resolution
Resolution means the resolving power of your imaging setup. Resolution is the smallest detail which is distinguishable in an image. The goal of most astro-imagers is that their images have the smallest details possible. Smaller resolution is better.
Resolving power includes the effects of diffraction limits, astronomical seeing, and defocus. The diffraction limit is determined by the aperture of your telescope. Astronomical seeing is beyond control aside from finding a better observing location. Only focus is subject to control during a given imaging session.
Ultimately, the quality of focus determines the resolving power you experience during a given imaging session. Better focus is better imaging resolution.
For comparative purposes, the following discussion assumes a 7-8" telescope aperture with an approximate diffraction limit of 0.6 arc seconds and good astronomical seeing for an amateur observing site of 2.0 arc seconds. The comparisons are representative of other telescope apertures, diffraction limits, and astronomical seeing.
Remember, smaller resolution is better. An overview of all focus techniques may be found at Focus Techniques.
GoldFocus Focusing System
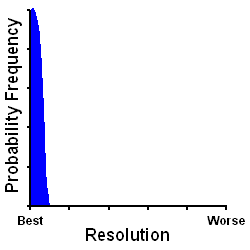
| Factor | arc seconds |
| Diffraction Limit | 0.6 |
| Astronomical Seeing | 2.0 |
| Defocus | < 0.05 |
| Total Resolution | 2.6 |
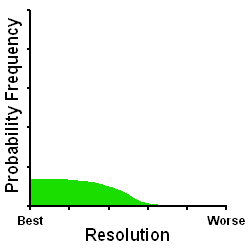
The GoldFocus Mask and Analysis Software consistently achieve near-perfect focus and therefore near-best resolution. The accuracy of focus can be less than 0.05 arc seconds resolution (depending somewhat on telescope and camera equipment) and for all practical purposes is negligible. The GoldFocus Focusing System allows you to image very near the diffraction and astronomical seeing limits of your telescope setup each and every time you image. The GoldFocus Focusing System achieves this accuracy because every aspect of the GoldFocus Mask and Analysis Software is designed toward achieving that specific goal.
Minimum FWHM
Minimum HFD
Minimum Sigma
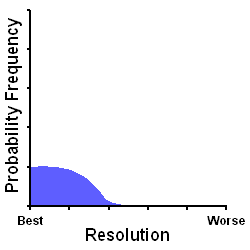
| Factor | arc seconds |
| Diffraction Limit | 0.6 |
| Astronomical Seeing | 2.0 |
| Defocus | 0.0 - 0.2 |
| Total Resolution | 2.6 - 2.8 |
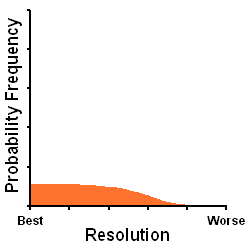
The Minimum FWHM, HFD, and Sigma techniques are hindered by the fact that they measure the total resolution of an image and therefore cannot distinguish the effect of defocus from temporal changes in astronomical seeing. Such short-term changes in seeing can be fairly significant and introduce error and uncertainty into the focus measures. In addition, the focus measures of the FWHM, HFD, and Sigma have 10-20 times less sensitivity than the measure used by GoldFocus. These techniques are aided by the fact that they are objective and computer assisted which allows them to take various steps to compensate for their disadvantages.
Bahtinov Mask
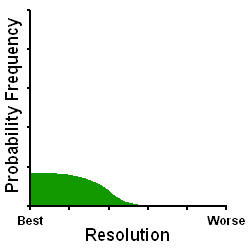
| Factor | arc seconds |
| Diffraction Limit | 0.6 |
| Astronomical Seeing | 2.0 |
| Defocus | 0.0 - 0.25 |
| Total Resolution | 2.6 - 2.85 |
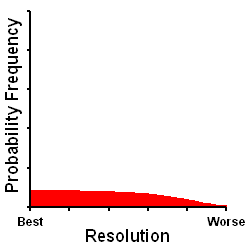
The Bahtinov Mask is probably the best visual subjective technique compared to currently available visual subjective focusing alternatives, not assisted by a computer analysis. The Bahtinov Mask technique is helped by the fact that it is largely unaffected by diffraction limits. On the negative side, the Bahtinov Mask is a visual subjective technique which is limited by the astronomer's ability (or inability) to subjectively assess diffraction spike positions with the level of precision required for truly good focus. The Bahtinov Mask is further hindered by astronomical seeing which blurs the diffraction spikes, making their precise positions all the more difficult to assess.
Diffraction Spike Mask
Modified Hartmann Mask
| Factor | arc seconds |
| Diffraction Limit | 0.6 |
| Astronomical Seeing | 2.0 |
| Defocus | 0.0 - 0.3 |
| Total Resolution | 2.6 - 2.9 |
The Diffraction Spike and Modified Hartmann Masks are very similar in their design and use. They are virtually indistinguishable in their focusing accuracy. Like the Bahtinov Mask, they benefit from being largely unaffected by diffraction limits. Conversely, the Diffraction Spike and Modified Hartmann Masks are visual subjective techniques which are limited by the ability to subjectively assess when diffraction spikes are coincident, or not, within the level of precision required for good focus. Their accuracy is further diminished by astronomical seeing which blurs the diffraction spikes, making the visual assessment all the more difficult.
"By Eye"
| Factor | arc seconds |
| Diffraction Limit | 0.6 |
| Astronomical Seeing | 2.0 |
| Defocus | 0.0 - 0.4 |
| Total Resolution | 2.6 - 3.0 |
The "By Eye" method uses an unobstructed image of a star. The star image size is affected by diffraction limits and astronomical seeing. The subjective visual assessment of quality of focus is difficult because the effect of focus is relatively small compared to the overall star image size and therefore difficult to visually and subjectively distinguish. It is probably being generous to say the "By Eye" method can reliably reduce the effects of defocus to less than 10-15% of the total of the diffraction limit and astronomical seeing.
Hartmann (Scheiner) Mask
| Factor | arc seconds |
| Diffraction Limit | 0.6 |
| Astronomical Seeing | 2.0 |
| Defocus | 0.0 - 0.5 |
| Total Resolution | 2.6 - 3.1 |
A little-known fact is that the Hartmann Mask is actually detrimental to good focus. The reason is that while the mask is in place, the effective aperture is reduced to the diameter of the Hartmann Mask holes, usually about one-quarter to one-third the telescope aperture diameter. Therefore, while the Hartmann Mask is in place, the diffraction limit of the image that the astronomer is using for focus is 3 to 4 times larger than the telescope's own diffraction limit. What the astronomer experiences during focusing with a Hartmann Mask is on the order of the following Representative Contributions to Resolution.
| Factor | arc seconds |
| Diffraction Limit | > 1.8 |
| Astronomical Seeing | 2.0 |
| Defocus | 0.0 - 0.5 |
| Total Resolution | 3.8 - 4.3 |
Because the Hartmann Mask is a visual subjective technique, it is more difficult for the astronomer to subjectively assess focus in the presence of more than 3.8 arc seconds of diffraction limit plus astronomical seeing compared to the total of 2.6 arc seconds diffraction plus seeing for an unobstructed "By Eye" image.
For example, if the astronomer is good enough to assess and reduce defocus to say 10% of the total of the diffraction limit and astronomical seeing of 3.8 arc seconds, then he will have defocus of 0.38 arc seconds with the Hartmann mask in place. Once the mask is removed, the focus stays the same but the total of diffraction and seeing is now 2.6 arc seconds. His final defocus of 0.38 arc seconds is nearly 15% of the total 2.6 arc seconds of diffraction and seeing. The astronomer is better off to use "By Eye" without a mask and get 10% of 2.6 arc seconds, or only 0.26 arc seconds defocus instead.